The fundamental 4 CS of critical thinking in education k-12
by Staff
What are the 4 C of critical thinking?
Critical thinking, as a concept and practice, can be framed in various ways. We can see, for example, by its function of social construction, its relationship with literacy, its necessity in political elections, etc.
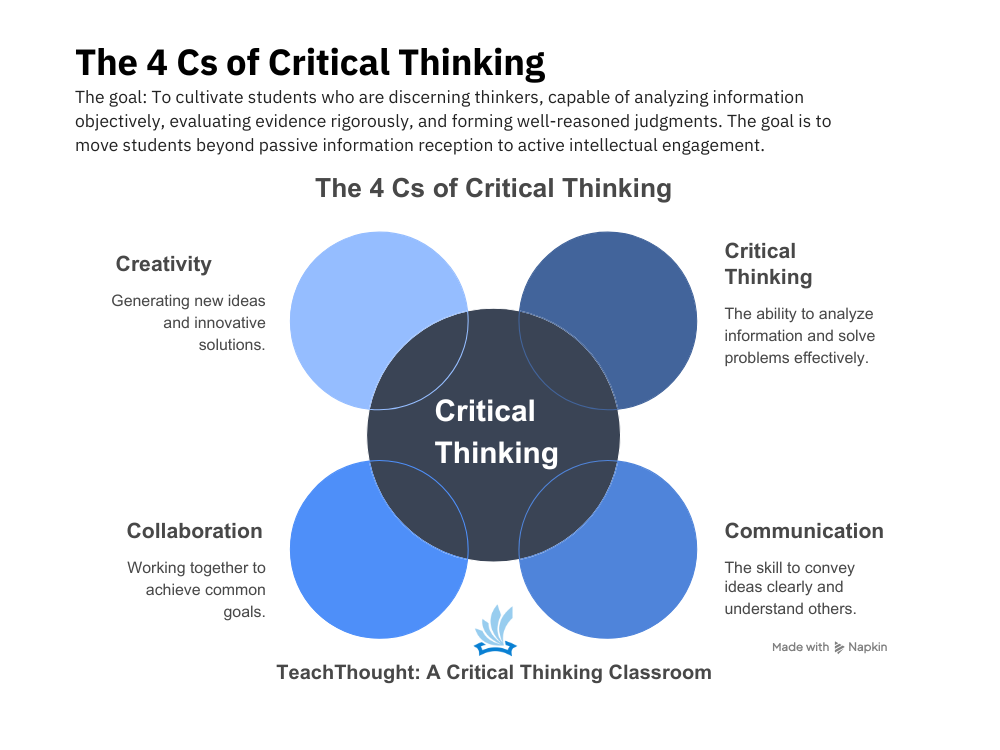
One of the most popular ways of the 4 tsp. Critical thinking, communication. Collaboration and creativity.
Critical thinking: The suspension of the judgment while identifying the biases and the underlying hypotheses in order to draw precise conclusions
Key features: proof, support, analysis, humility, clarity, flexibility
Communication
To communicate is clearly and deliberately expressing ideas, questions and reasoning in a way that can be understood, evaluated and reacted constructively. This implies not only to speak or write, but but Translate thought in formRecognize the public and use evidence and a logic to support clarity and precision.
Key features: clarity, consistency, logical structure, reactivity to feedback.
Collaboration
Collaboration is the intentional process of engaging with others to explore ideas, challenge thought and co-build the meaning or solutions. It requires opening up to various perspectives, respectfully assess the argumentsand construction consensus according to reason and evidence, not just the agreement.
Key features: active listening, shared reasoning, respectful disagreements, joint problem solving.
Creativity
Creativity is the ability to generate original, flexible and effective ideas by connecting concepts in a new way. It’s not just a question of expression, but by the way Innovative problem solving—Acting of hypotheses, exploring alternatives and building new understanding frames.
Key features: Divergent thought, intellectual risk taking, synthesis, originality with goal.
See also The definition of a Socratic seminar

Definition of 4 CS
1. Critical thought
The idea: cultivate students who are demanding thinkers, capable of objectively analyzing the information, rigorously assess the evidence and to train well prosecuted judgments. Hope is to move students beyond the passive reception of information to active intellectual engagement.
Short definition: analyze information and identify underlying biases and hypotheses to draw precise conclusions. As we said previously, “critical thinking implies” suspension of judgment during information analysis “to achieve well supported understanding.
Advantage: critical thinking allows students to become independent learners and problem solvers. They develop the ability to question, investigate and make informed decisions, essential skills for academic success and navigate life beyond the class.
See The definition of critical thinking
Classy
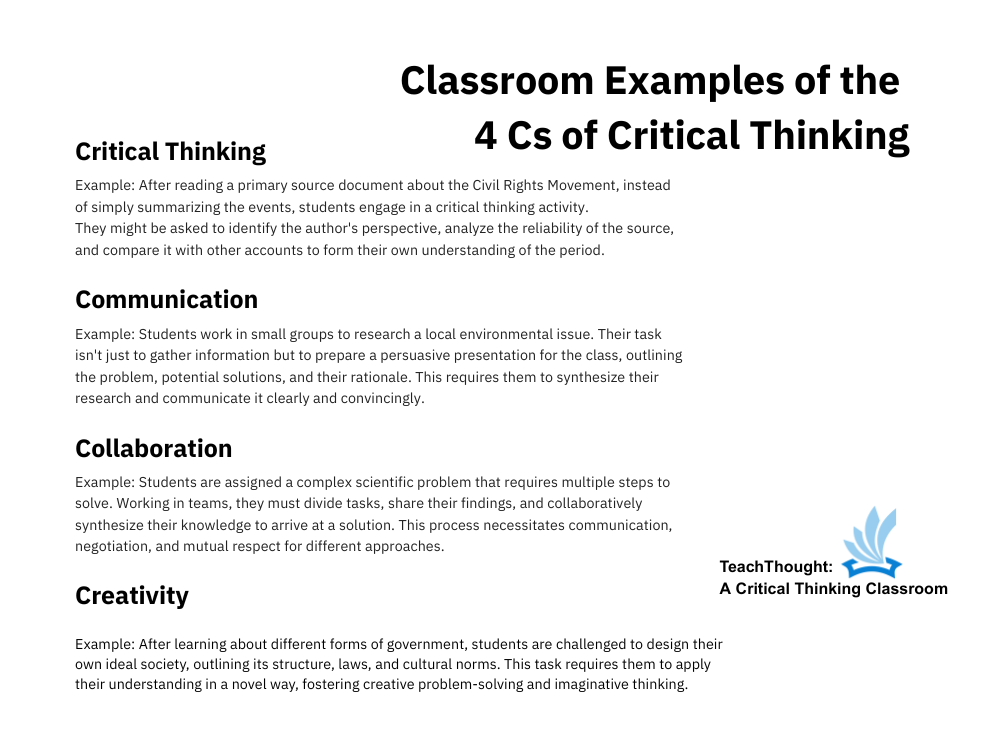
After reading a primary source document on the civil rights movement, instead of simply summing up events, students engage in a critical thinking activity.
They could be asked to identify the author’s point of view, to analyze the reliability of the source and to compare it with other accounts to train their own nuanced understanding of the period.
2. Communication
The idea: to develop students who can effectively articulate their thoughts and ideas, both orally and in writing, with clarity, consistency and objective. We aim that students can transmit complex information and initiate a significant dialogue with a diversified audience.
Short definition: Express ideas, thoughts and information clearly and effectively through various supports (oral, written, visual, digital).
Advantage: Strong communication skills allow students to share their understanding, to collaborate effectively and to actively participate in their learning community. The ability to articulate their reasoning is intrinsically linked to critical thinking, allowing them to explain Why They reached a particular conclusion.
Classy
Students work in small groups to seek a local environmental problem. Their task is not only to collect information but to prepare a persuasive presentation for the class, describing the problem, the potential solutions and their justification. This forces them to synthesize their research and to communicate it clearly and convincingly.
3. Collaboration
The idea: to grow students who can work effectively and respectfully with others to achieve common goals. We aim to develop their ability to share ideas, negotiate, compromise and contribute their unique forces within a team.
Short definition: work in cooperation with others, share ideas and contribute to a collective effort to achieve a shared objective.
Advantage: collaboration improves learning by exposing students to various perspectives and promoting shared understanding. It reflects real world scenarios where problem solving often requires teamwork and the ability to take advantage of different skills and points of view. Research highlights the link between collaborative learning and the improvement of critical thinking skills (Johnson and Johnson, 2009).
Classy
Students are assigned a complex scientific problem that requires several steps to be resolved. Working in teams, they must divide the tasks, share their results and synthesize their knowledge in collaboration to reach a solution. This process requires communication, negotiation and mutual respect for different approaches.
4. Creativity
The idea: Cultivate students who are innovative thinkers, capable of generating new ideas, exploring possibilities and approaching challenges with imagination and originality. We aim to feed their ability to “think outside the box” and find unique solutions.
Short definition: Generate new ideas, establish new connections and approach tasks with imagination and originality.
Advantage: Creativity allows students to approach problems from fresh angles and develop unique solutions. It promotes innovation and adaptability, crucial skills in a rapidly evolving world. Building in creative tasks can also deepen understanding and make learning more memorable.
Classy
After learning the different forms of government, students are challenged to design their own ideal society, describing its structure, its laws and its cultural norms. This task obliges them to apply their understanding in a new way, promoting the creative resolution of problems and imaginative thought.
Works cited
Johnson, DW and Johnson, RT (2009). An elaboration of psychological interdependence. Psychological Bulletin, 135(2), 282–318.
Gay, G. (2018). Culturally sensitive teaching: theory, research and practice (3rd ed.). Teachers College Press.
Teachthought’s mission is to promote critical thinking and innovation education.



